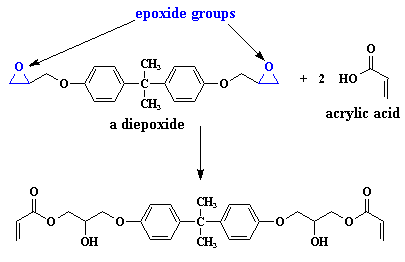
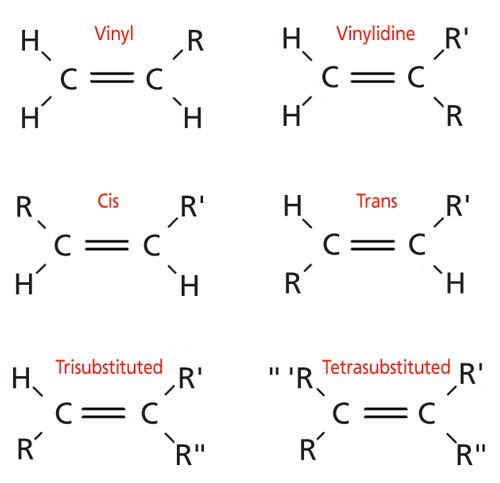
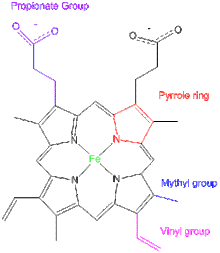
In chemistry vinyl or ethenyl abbreviated as vi is the functional group with the formula c h ch 2 it is the ethylene iupac ethene molecule h 2 c ch 2 with one fewer hydrogen atom.
Examples of vinyl groups.
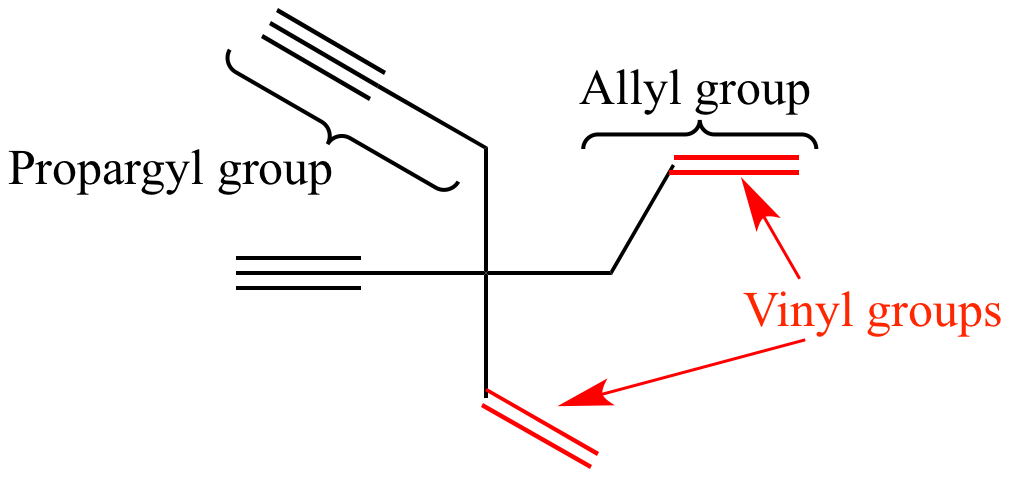
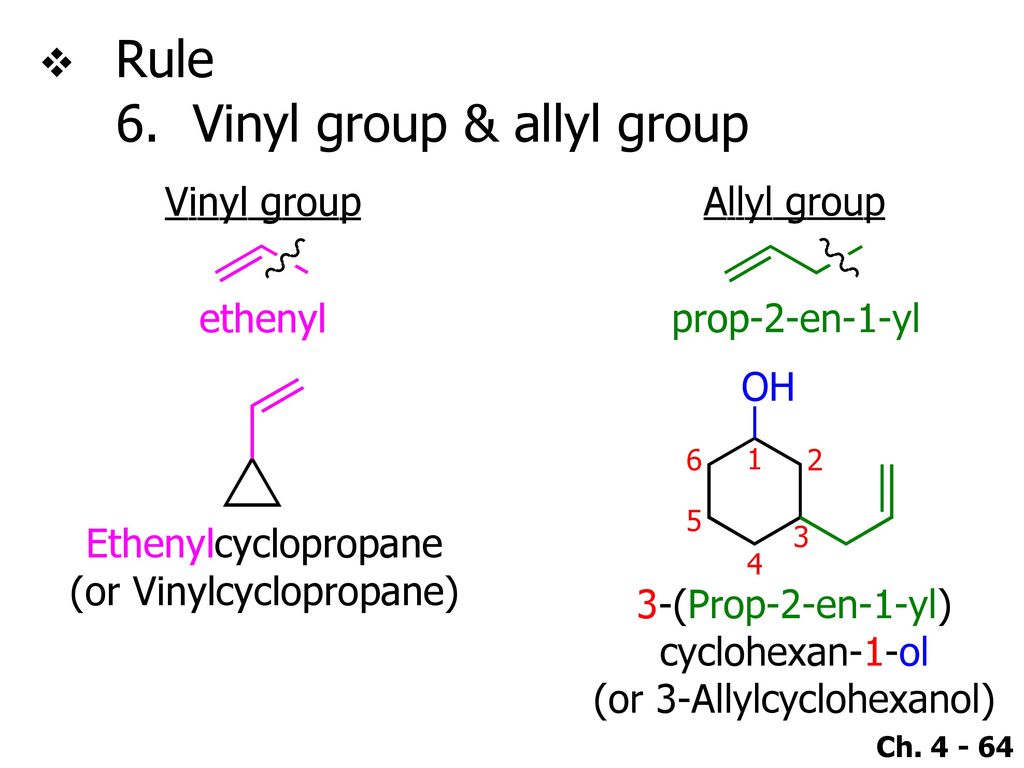
In vinyl group c c is directly attached to the rest of the chain.
Functional groups can pertain to any molecules but you will usually hear about them in the context of organic chemistry the symbol r and r refer to an attached hydrogen or hydrocarbon side chain or sometimes to any group of atoms.
In contrast to vinyl allyl group is attached to the rest of the molecule through ch 2 group.
It is used as a precursor to manufacture polyvinyl chloride pvc.
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed.
The name is derived from the latin word for garlic allium sativum in 1844 theodor wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it schwefelallyl.
This is the main difference between allyl and vinyl groups.
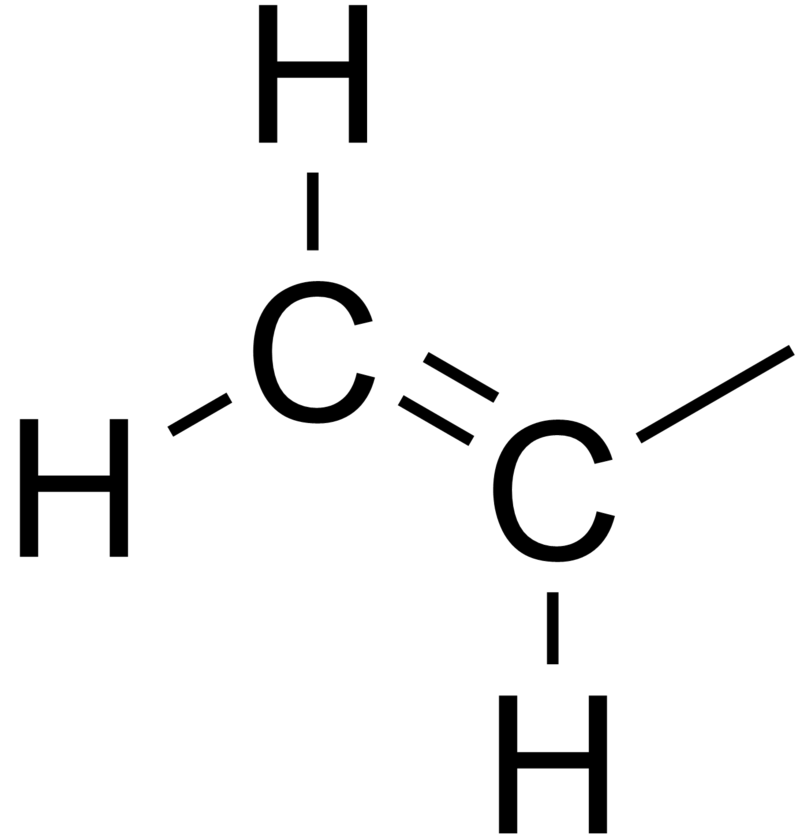
H 2 c ch ethenyl or commonly known as vinyl.
It imparts unique chemical properties to allylic group and presence of this group in different compounds form allylic compounds which are used for the preparation of different natural products like natural rubber terpenes etc.
One of the best examples of an industrial application of vinyl group is vinyl chloride ch 2 ch cl.
An alkenyl group is a hydrocarbon group formed when a hydrogen atom is removed from an alkene group.
An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule.
Alkenyl compounds are named by replacing the e from the parent alkene s name with yl.
Functional groups are groups of atoms found within molecules that are involved in the chemical reactions characteristic of those molecules.
It is the third most widely produced synthetic plastic variety in the world.
An electron donating group edg or electron releasing group erg z in structural formulas is an atom or functional group that donates some of its electron density into a.
That is to join end to end forming a polyvinyl compound such as polyvinyl chloride.
The name is also used for any compound containing that group namely r ch ch 2 where r is any other group of atoms.
Vinyl compounds contain the hydrocarbon vinyl group ch 2 ch.
Vinyl indicates the ch ch 2 functional group which can be formed by removing hydrogen from ethylene.
Unlike vinyl group the allylic carbon atom is sp 3 hybridized as it bonded with ch ch 2 through a single covalent bond.
The molecules of two different compounds can also be made to link up forming a copolymer such as the plastic vinylite and the.